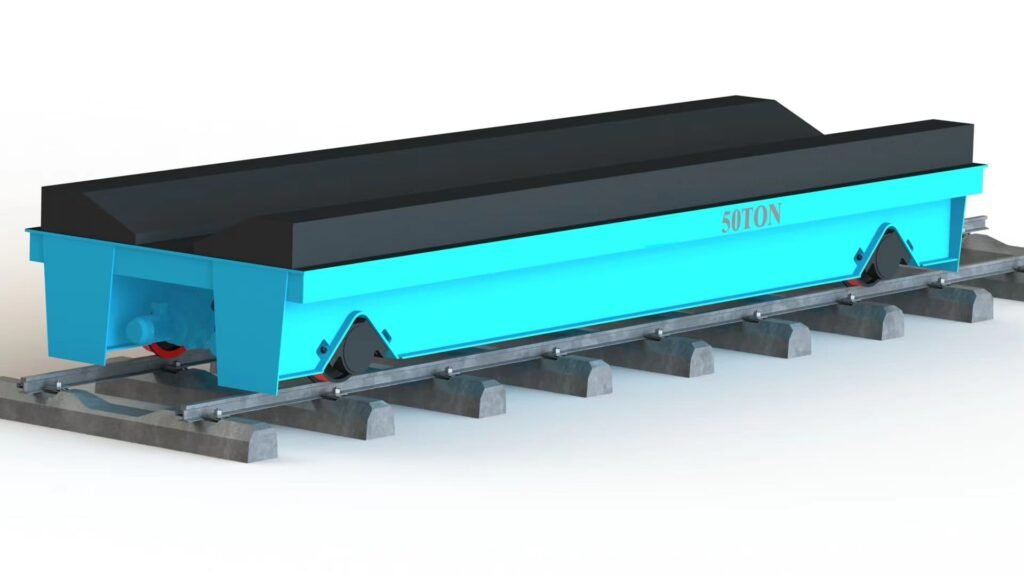
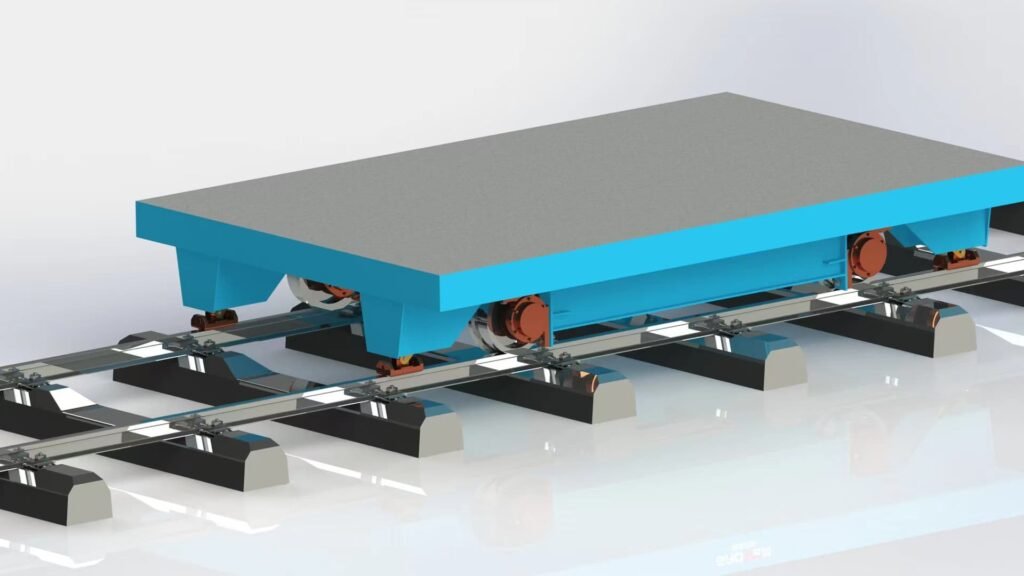
Rail transfer carts, also known as rail-guided transfer trolleys or rail-bound transfer carts, are specialized material handling vehicles designed to move heavy loads along a fixed rail system. These carts are commonly used in various industrial settings, including manufacturing plants, warehouses, and assembly lines, where the transportation route is predefined and repetitive. Here’s a detailed look at rail transfer carts
Key Features
- Design and Construction
Sturdy Frame Made of high-strength steel to handle substantial weights and ensure durability.
Rail Wheels Fitted with wheels designed to run on steel rails, providing stability and smooth movement. - Power Source
Electric Powered Typically powered by electricity, either through an onboard battery system or connected to the facilitys power grid via a cable.
Battery Operated Offers flexibility within the rail network without the need for constant power connection.
Cable Reel Powered Uses a cable reel to supply continuous power from a fixed point. - Load Capacity
Can handle a wide range of loads, from a few tons to several hundred tons, depending on the carts design and application. - Guidance System
Rail-Guided Moves strictly along the installed rails, ensuring precise and predictable paths.
Functions and Applications
- Material Handling
Efficiently transports raw materials, work-in-progress, or finished products between different stages of production or storage areas. - Assembly Line Integration
Transfers components along various stages of an assembly line, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries. - Warehouse Logistics
Facilitates the movement of heavy items in warehouses, often integrated with automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS). - Loading and Unloading
Moves materials between different parts of a facility or to/from transportation vehicles such as trucks or other rail systems.
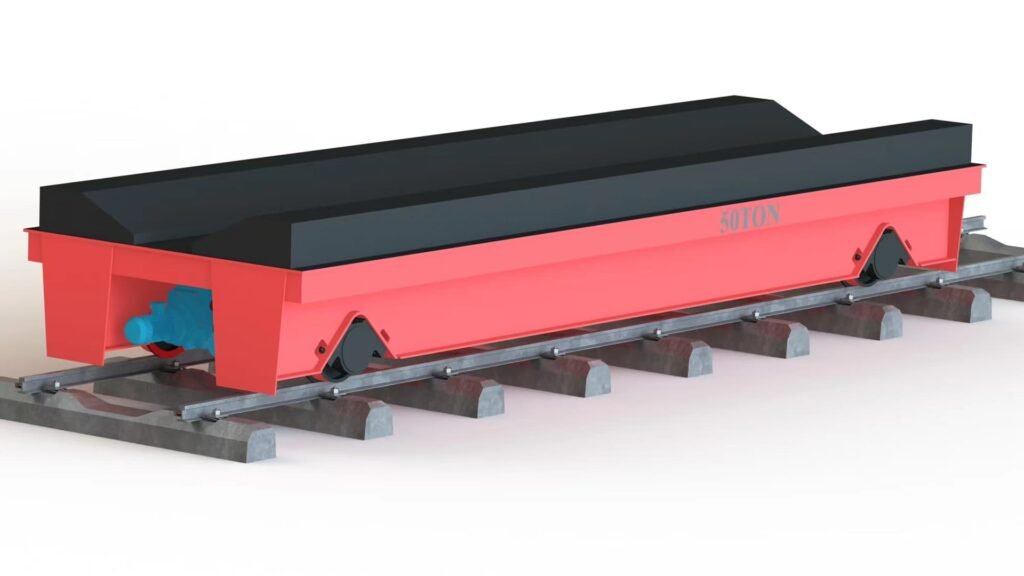

Types of Rail Transfer Carts
- Single-Rail Carts
Run on a single track, typically used for straightforward linear movement. - Double-Rail Carts
Operate on parallel tracks, providing enhanced stability for very heavy or oversized loads. - Turntable Rail Carts
Equipped with a turntable to switch tracks or change directions, allowing for more complex movement paths within a facility. - Custom Rail Carts
Tailored to specific industry needs, which may include special dimensions, capacities, or additional features such as tilting platforms or rotating decks.
Advantages
- High Load Capacity
Capable of transporting extremely heavy and bulky items with ease. - Precision and Safety
The fixed rail system ensures precise movement and reduces the risk of accidents associated with free-moving vehicles. - Efficiency
Ideal for repetitive and high-volume transport tasks, enhancing overall operational efficiency. - Customizability
Can be designed to meet specific requirements, including size, shape, and additional functionalities. - Low Maintenance
Generally robust and durable, requiring minimal maintenance compared to other types of transport systems.
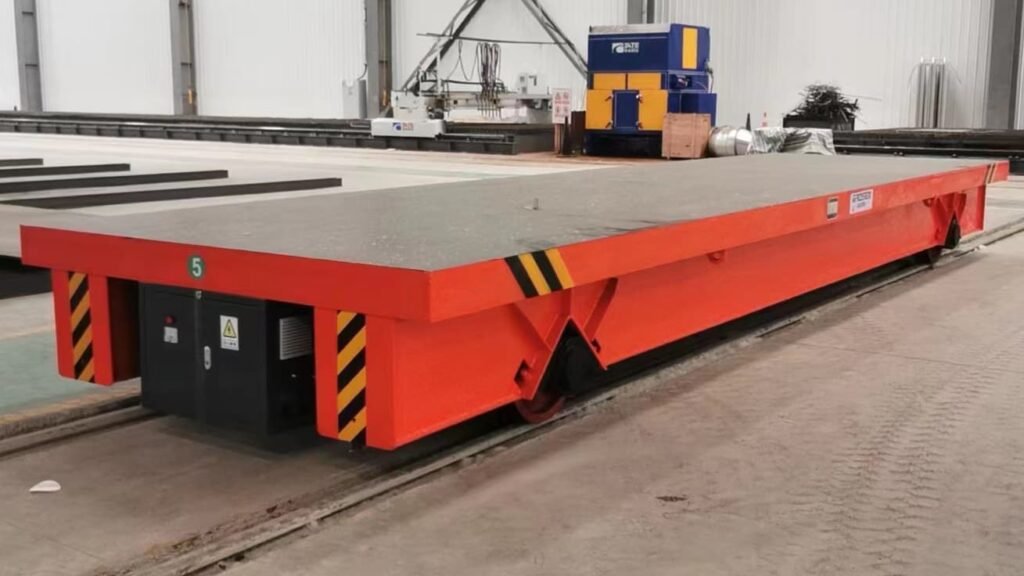

Limitations
- Fixed Path
Limited to predefined routes, lacking the flexibility to change paths or routes easily. - Infrastructure Requirement
Requires the installation of a rail system, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Use Cases
- Steel Plants
Moving large steel coils or slabs between processing areas. - Automotive Manufacturing
Transporting car bodies or large components through various stages of assembly. - Shipbuilding
Handling heavy ship sections or components within the yard. - Mining Operations
Moving extracted ore or heavy equipment between different processing areas.
Rail transfer carts are essential in environments where high-capacity, repetitive, and reliable transportation of heavy loads is required. Their robust design and ability to integrate with industrial processes make them a valuable asset in many heavy-duty material handling applications.
